Vapor Pressure of Gasolines (Reid Diagram)
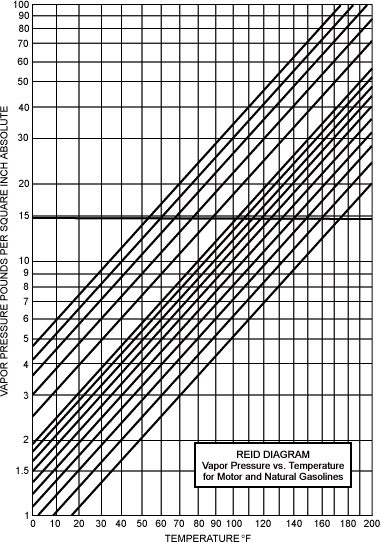
| To determine
the gage working pressure of a vessel to store any natural
gasoline: 1. Determine the maximum liquid surface temperature reached (or likely to be reached) by the liquid during the period of storage. 2. The vertical temperature line intersects the Reid vapor pressure line for the liquid being considered at a definite point. 3. From the curve determine the initial vapor pressure in pounds absolute at the left-hand side horizontally from the intersection mentioned in Step 2. 4. Subtract 14.7 from the initial vapor pressure in pounds absolute. The result is the gage working pressure of the vessel required to store the gasoline without evaporation loss. |
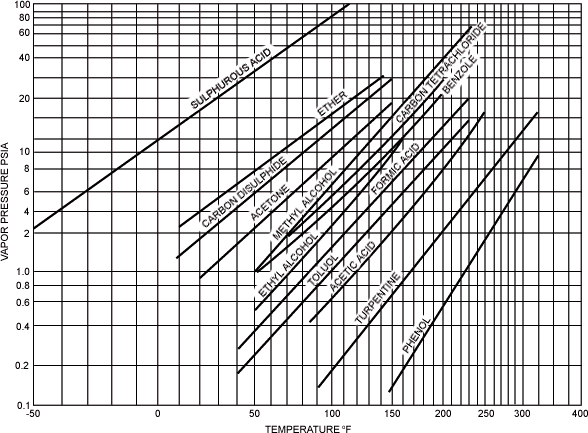
Vapor Pressure of Miscellaneous Liquids
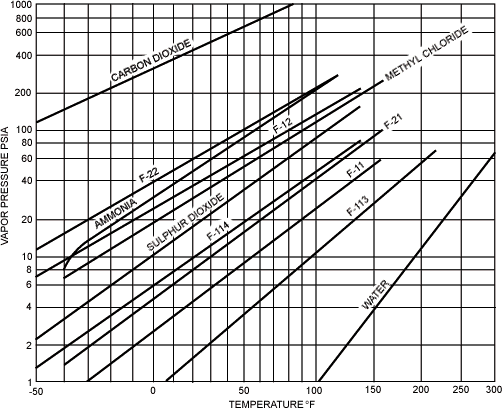
Vapor Pressure of Refrigerant Liquids
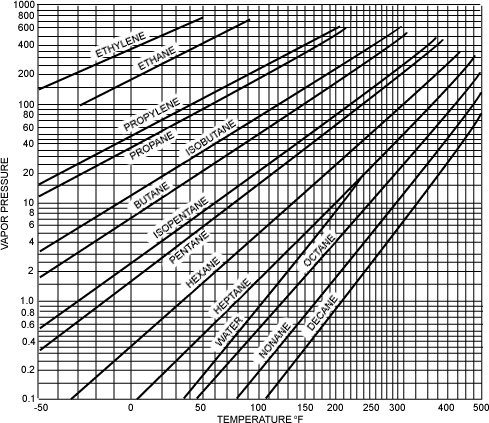
Vapor Pressure of Selected Hydrocarbons
Volatile -- Vapor Pressure and Specific Gravity
Temp
¢µ |
Ammonia |
Carbon Dioxide |
Freon-12 |
Butane |
Propane |
|||||
Vapor
Press psia |
Spec grav |
Vapor
Press psia |
Spec grav |
Vapor
Press psia |
Spec grav |
Vapor
Press psia |
Spec grav |
Vapor
Press psia |
Spec grav |
|
| -60 | 5.6 | 0.70 | ||||||||
| -50 | 7.7 | 0.70 | ||||||||
| -40 | 10.4 | 0.69 | 9.3 | 1.51 | 16.2 | 0.58 | ||||
| -30 | 13.9 | 0.8 | 12.0 | 1.50 | 20.3 | 0.57 | ||||
| -20 | 18.3 | 0.68 | 220.6 | 1.03 | 15.3 | 1.48 | 25.4 | 0.57 | ||
| -10 | 23.7 | 0.67 | 261.7 | 1.01 | 19.2 | 1.47 | 31.4 | 0.56 | ||
| 0 | 30.4 | 0.66 | 308.6 | 0.99 | 23.9 | 1.45 | 7.3 | 0.62 | 38.2 | 0.55 |
| 10 | 38.5 | .066 | 361.8 | 0.97 | 29.4 | 1.43 | 9.2 | 0.61 | 46.0 | 0.55 |
| 20 | 48.2 | 0.65 | 422.0 | 0.95 | 35.8 | 1.42 | 11.6 | 0.61 | 55.4 | 0.54 |
| 30 | 59.7 | 0.64 | 489.7 | 0.92 | 43.2 | 1.40 | 14.4 | 0.60 | 66.3 | 0.53 |
| 40 | 73.3 | 0.63 | 565.0 | 0.89 | 51.7 | 1.38 | 17.7 | 0.60 | 78.0 | 0.52 |
| 50 | 89.2 | 0.63 | 650.1 | 0.85 | 61.4 | 1.36 | 21.6 | 0.59 | 91.8 | 0.52 |
| 60 | 107.6 | 0.62 | 744.3 | 0.81 | 72.4 | 1.34 | 26.3 | 0.59 | 107.1 | 0.51 |
| 70 | 128.8 | 0.61 | 848.8 | 0.76 | 84.8 | 1.32 | 31.6 | 0.58 | 124.0 | 0.50 |
| 80 | 153.0 | 0.60 | 964.4 | 0.68 | 98.8 | 1.30 | 37.6 | 0.57 | 142.8 | 0.49 |
| 90 | 180.6 | 0.59 | 114.3 | 1.28 | 44.5 | 0.56 | 164.0 | 0.48 | ||
| 100 | 211.9 | 0.58 | 131.6 | 1.26 | 52.2 | 0.56 | 187. | 0.47 | ||
| 110 | 247.0 | 0.57 | 150.7 | 1.24 | 60.8 | 0.55 | 213.0 | 0.46 | ||
| 120 | 286.4 | 0.56 | 171.8 | 1.22 | 70.8 | 0.54 | 240.0 | 0.45 | ||
Copyright(C)
pumpia All Right Reserved .